Otorrhea: A Comprehensive Overview
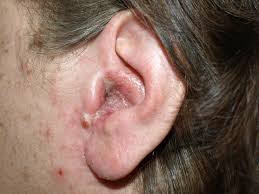
Otorrhea is a medical condition in which there is discharge from the ear, whether it is watery, pus-filled, or bloody. This symptom can be an indication of a variety of medical conditions that range from mild to serious.
Common causes of ear discharge:
- Otitis media: This is an infection of the middle ear and is usually caused by bacteria or viruses.
- Rupture of the eardrum: This rupture may be caused by an infection, injury, or sudden change in air pressure.
- Foreign bodies: A foreign body entering the ear can cause irritation and discharge.
- Fungal infection: A fungal infection may affect the ear, especially in people who use ear drops frequently or who have a weakened immune system.
- Tumors: In rare cases, ear discharge may be a sign of a tumor in the ear or sinuses.
Associated symptoms:
- Pain: There may be pain in the affected ear.
- Itching: The affected person may feel itchy inside the ear.
- Feeling of ear blockage: The affected person may feel full or blocked in the ear.
- Hearing loss: Ear runny nose may lead to partial or complete hearing loss.
- Dizziness: The affected person may feel dizzy or throbbing.
Diagnosis:
Ear runny nose is diagnosed through a physical examination of the ear using an otoscope, in addition to performing some other tests such as:
- Hearing test: to assess the extent of the infection's impact on hearing.
- Examination of secretions: to determine the type of organism causing the infection.
- CT scan or MRI: In some cases, these tests may be necessary to assess the condition of the inner ear and surrounding structures.
Treatment:
Treatment of ear runny nose depends on the underlying cause, and may include:
- Antibiotics: to treat bacterial infections.
- Ear drops: to treat fungal or bacterial infections.
- Pain relievers: to relieve pain.
- Surgery: in cases that require surgical intervention, such as removing foreign bodies or repairing a ruptured eardrum.
Important note:
A doctor should be consulted to diagnose and treat ear runny nose, as delaying treatment may lead to serious complications.